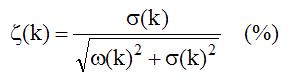
Modal frequency is listed as the damped natural frequency in the Modal Parameters spreadsheet
w(k) = damped natural frequency of mode (k) (in Hz)
Modal damping is listed as the damping ratio or percent of critical damping in the Modal Parameters spreadsheet
The damping ratio for mode (k) is defined as,
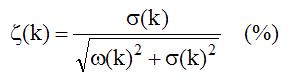
Modal damping is also listed as the Half Power Point (3 dB bandwidth) or Damping Decay Constant in the Modal Parameters spreadsheet
The damping decay constant for mode(k) is defined as,
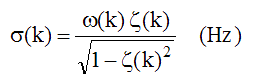
The undamped natural frequency for mode(k) is defined as,
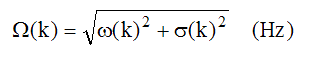
The half power point damping for mode(k) is defined as,
![]()
The half power point damping is the width of a resonance peak. It is derived from a single mode definition of an FRF
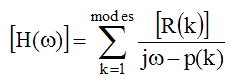
Evaluating the single mode FRF at the frequency of mode(k) gives,
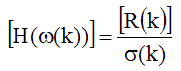
Power is obtained by squaring the FRF,
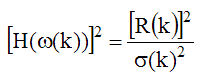
Equating half of this value to the square of the single mode FRF gives,
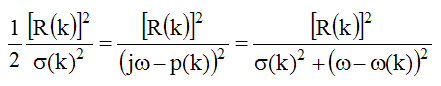
Solving the above equation gives two frequencies at which the FRF power equals half of its value at the resonant frequency. These two frequencies are called the half power points,
![]()
The width of the resonance peak between the two half power points is equal to twice the modal damping decay constant,
![]()
The half power points are also 3 dB less than the power at the resonance peak, This bandwidth estimate of modal damping is also called the 3 dB bandwidth damping.
The width of the resonance peak in an FRF at 70.7% of its magnitude at the peak is equal to twice the damping decay constant.
The wide of a resonance peak is a measure of the damping of a mode. The wider the peak, the greater the damping.
The Loss factor h(k) is equal to twice the percent of critical damping.
![]()
The Quality factor Q(k) is the inverse of the Loss factor.
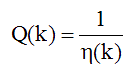
The four definitions of modal frequency & damping are plotted on the top view of the S-plane (or complex frequency plane) below.
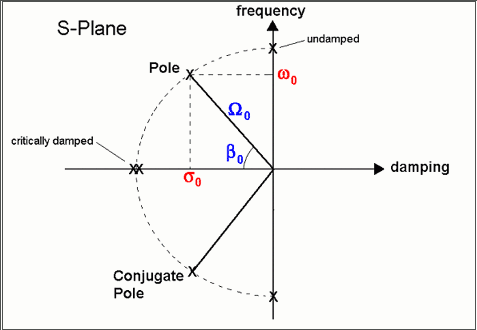
S-plane Showing Modal Frequency & Damping Terms.
In summary, modal frequency & damping are defined in several different ways,
p(k) = -s(k) + jw(k) = pole location of mode(k) (Hz)
w(k) = damped natural frequency of mode(k) (Hz)
s(k) = damping decay constant (also called the 3 dB bandwidth or half power point damping) of mode(k) (Hz)
z(k) = damping ratio
W(k) = undamped natural frequency of mode(k) (Hz)
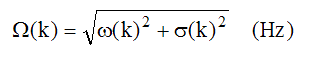
|
Half Power Point Bandwidth (3 dB Bandwidth) |
|
|
Damping Ratio (Percent of Critical) |
|
|
Decay Constant |
|
|
Loss Factor |
|
|
Quality Factor |
|